Appearance
二维数组遍历技巧
旋转矩阵
先将矩阵按对角线交换(正序和倒序旋转选取的对角线不同),然后反转二维数组的每一行。
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=48 lang=java
*
* [48] 旋转图像(顺时针)
*/
// @lc code=start
class Solution {
public void reserve(int[] arr) {
int i = 0, j = arr.length - 1;
while (j > i) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i++] = arr[j];
arr[j--] = temp;
}
}
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
// 先将二维数组按对角线交换
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
int temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i] = temp;
}
}
// 然后反转二维数组的每一行
for (int[] row : matrix) {
reserve(row);
}
}
}
// @lc code=end
矩阵的螺旋遍历
核心思路是按照右、下、左、上的顺序遍历数组,并使用四个变量圈定未遍历元素的边界,随着螺旋遍历,相应的边界会收缩,直到螺旋遍历完整个数组。
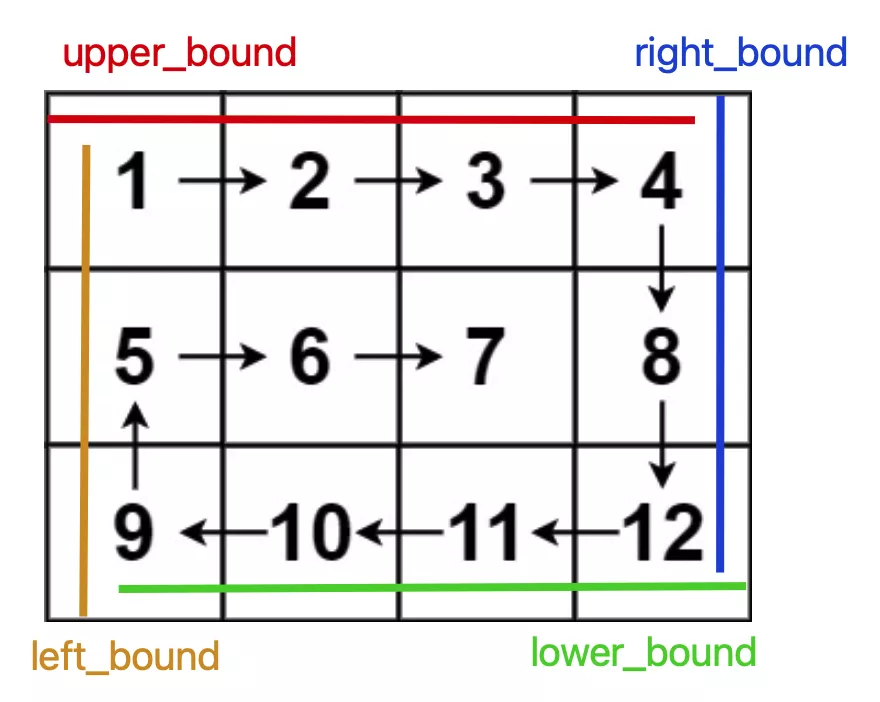
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/*
* @lc app=leetcode.cn id=54 lang=java
*
* [54] 螺旋矩阵
*/
// @lc code=start
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int left_bound = 0, right_bound = n - 1;
int top_bound = 0, bottom_bound = m - 1;
List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
while (res.size() < m * n) {
// 顶部的边界值小于底部的边界,则从顶部从左到右遍历
if (top_bound <= bottom_bound) {
for (int i = left_bound; i <= right_bound; i++) {
res.add(matrix[top_bound][i]);
}
// 移动上边界
top_bound++;
}
// 接着在右侧从上到下遍历
if (left_bound <= right_bound) {
for (int i = top_bound; i <= bottom_bound; i++) {
res.add(matrix[i][right_bound]);
}
// 移动右边界
right_bound--;
}
// 从底部从右到左遍历
if (top_bound <= bottom_bound) {
for (int i = right_bound; i >= left_bound; i--) {
res.add(matrix[bottom_bound][i]);
}
// 移动下边界
bottom_bound--;
}
// 接着在左侧从下到上遍历
if (left_bound <= right_bound) {
for (int i = bottom_bound; i >= top_bound; i--) {
res.add(matrix[i][left_bound]);
}
// 移动左边界
left_bound++;
}
//这样子就已经遍历了外圈,接着遍历内圈,直到全部遍历完成。
}
return res;
}
}
// @lc code=end
 Code More Create
Code More Create